푸리에 식의 각각의 구성 성분이 같은 값으로 줄어들면, 진폭은 줄어들지 언정 왜곡되지 않는다 (직사각형 깔끔한 모양)
하지만 모든 전송 설비는 각 구성 성분값을 다르게 변화 시키므로, 왜곡이 유발된다. 보통의 와이어들은 0부터 어느정도의 구역까지는 왜곡되지 않음.
강하게 왜곡 돼지 않고 전송된 주파수 대역을 대역폭이라고 하는데 보통 0에서 수신전력의 절반까지의 주파수를 말한다.
대역폭은 구성, 두께 및 길이의 의존하는 전송 매체의 물리적 특성
The bandwidth is the width of the band of frequencien thar are passed.
The information that can be carried is depending on the width.
Baseband : 0 to max freq
Passband : Signals shifted to occupy a higher range of freq for wireless communication.
Purpose of Physical layer : send bits to the other system.
Magnetic Media: Use portable device like CD. The cost and bandwidth are faster/cheaper than any network. However, delay isn’t good (as it cannot be the live communication).
Twisted Pair: It is twisted to avoid constituting antenna (twisted cancel the waves hence lose less wire). Signal is carried by the diff between the two wires.
- Telephone: need repeater if the distance longer than few kilometers.
- Transmitting information: several mb/s for a few kilo. Adequate performance and cheap cost ⇒ will be used
** Different LAN protocol use the twisted pair differently.
- Full-duplex : in both direction at the same time.
- Half-duplex : one direction at once - can change the direction.
- Simpelx : only one way traffic.
** cat 5: LAN, cat 6: UTP, cat 7: STP
Coaxial Cable: better than UTP in shielding and greater bandwidth ⇒ longer distances at higher speed.
- Construction and shielding ⇒ high bandwidth and excellent noise immunity.
- Was widely used for phone cable which now replaced by fiber optics for long routes.
Power Lines - data signal is superimposed on the low freq power signal (the high frequency works as the normal power line).
Fiber Optics - costs expensive and costs more energy to send bits. FTTH (Fiber to the Home).
- Light Source
- Transmission Medium
- Detector
The light is refracted (bounced within the cable) while maintaining certian angle. Hence, propagate for many kilometers without any loss.
Multimode fiber: multiple rays within the line.
Singlemode fiber: one straight ray due to the small diameter of the cable (100 Gbps for 100 km).
Transmission of Light-FiberChromatic Dispersion (length of the wave gets longer) - 겹치지 않기 위해서는 서로간의 거리를 늘려야 하나, 속도를 줄이는 방법만 가능. Soliton 이라는 특수 형태의 펄스를 만들어 분산 효과를 상새하는 방법을 사용중.
Fiber Cable - core is surrounded by glass cladding to maintain the light.
- Plugged into fiber socket: Lose about 10~20% but easy to reconfigure.
- Spliced mechanically: carefully cut two ends and connect with special sleeve; lose 10%
- Fused (melted) to form one: small amount of attenuation (손실) occurs.
Comparison of Fiber Optics and Copper Wire
Fiber
1.Can handle higher bandwidth ⇒ can be used in high-end network.
2.Low attenuation ⇒ need of repeater every 50km (copper: 5km) → save costs
3.Not interfered by power surge, electromagnetic interference, or power failures → good for harsh env.
4.Thin and lightweight → phone companies like it. Good replacement for copper and they can resale copper and also cheaper to installation and maintain cost.
5.Do not leak and are difficult to tap - good security.
- 친숙치 않은 기술, 휘어지면 쉽게 손상 가능, 본질적으로 단방향이므로 2개의 섬유 또는 2개의 주파수 필요. 전기 인터페이스보다 비쌈.
Week 2/2 - Wirelsee Communication.
The Electromagnetic Spectrum - wave caused by movement of electron. The num of oscillations per second = Frequency in unit of Hz. Wavelength : distance between cosecutive maxima/minima.
apprpriate antenna size - electromagnetic waves can be broadcast efficiently.
In a vaccum - all elecmagnetic travel at the same speed (speed of light). → copper : 2/3 of this speed.
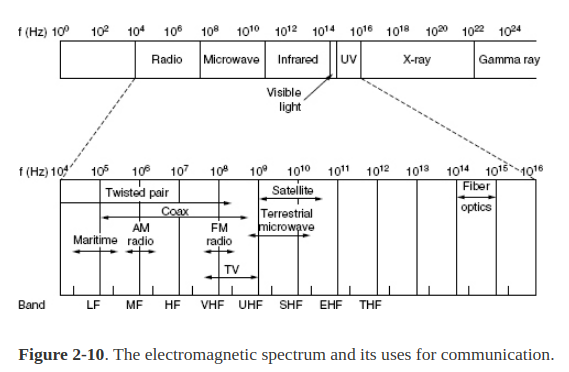
Mostly use narrow frequency band - concentrate signals to use the spectrum efficient and to obtaion reasonable data rate with enough power.


